TOKENIZATION, NFTs
Tokenization:
- What is Tokenization?
- Meaning of Digitization
- How Digitization is different from Tokenization?
- Future of Tokenization
NFTs (Non-Fungible Assets):
- Meaning of Fungible assets
- Meaning of Non-fungible assets
- Meaning of Non-fungible tokens
- How NFTs accrue values?
- Are NFTs a Fad?
- Future of NFTs
- How to buy NFTs?
- Use cases of NFTs
- Story of CryptoKitties
- Popular FAQs :
Ø What is Minting in NFTs ?
Ø What are the legal rights of the buyer of NFT?
Ø Why do we need NFTs in IP market ?
Ø What are the types of NFTs
Ø Popular characteristics of NFTs
- NFT Standards
TOKENIZATION
It’s an important term liked by majority of the people in crypto world.
Let’s discuss what does it mean?
I would prefer to combine ‘Tokenization’ with another term ‘Digitization’.
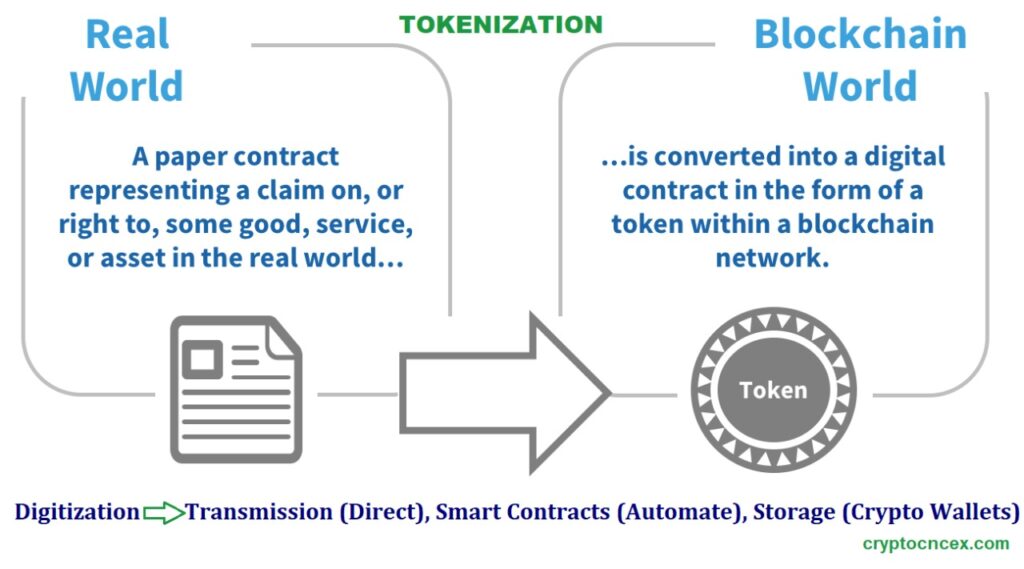
Digitization : Let’s go in to past when most of the financial transactions used to be on a piece of paper. Ex- share certificates used to be on a paper like security paper if you remember or have seen, Fixed deposits receipts (FDR) used to be issued on a piece of paper, Pass book on a paper like a booklet which is still in use. But during 1990s onwards in India, with computers came and internet introduced, digitization of financial documents was started with slow speed. Shares certificates were digitized and D-MAT accounts were introduced where shares with their distinctive serial numbers were issued digitally. FDRs were digitized. Passbooks also were digitized like bank statement in soft copy (i.e. e-statement).
How Digitization is different from Tokenization :
Digitization is a ‘Dumb’ act which means conversion of paper data in to digital format without involving any element of intelligence.
Tokenization has vast meaning but here at least is taking digital assets like pictures, documents, pdfs or various other formats like movies etc. and adding some intelligence to such digital assets. Here intelligence is to fractionize such digital assets in to parts. Ex- Reliance share of Rs. 2000 per share fractioned in to parts (Tokenized) and now we can buy 100th part of this digital format of Reliance share @Rs. 20 also after it’s tokenization.
Tokenization is one step beyond digitization.
Three important aspects of tokenization are ‘Storage’, ‘Transmission’ & ‘Smart Contracts’.
In crypto world, way of Transmitting tokens from one party to another is direct which means without involving 3rd party or middleman or service provider like in digital world we transfer money from one party to another through a bank as middleman but in crypto world, there is no need of middlemen to transmit crypto money (I mean tokens here). I can transfer tokenized image directly to you. This is also called peer-to-peer transmission.
Another aspect is Storage. We can store tokenized digital assets in to crypto wallets from where we can transfer tokenized crypto assets to another crypto wallet. We can also receive tokenized assets in our crypto wallets from other crypto wallets.
Smart contracts here means embedding self executing instructions in to the tokenized digital asset. In case of every sale of tokenized image, if instructions of royalty to be paid to the creator/owner at some fixed % of sale price or whatever are already there through smart contract, then automatically royalty will be transferred to the concerned owner/creator with every sale of tokenized image.
Future of Tokenization : Everything that can be tokenized will be tokenized. Like today in digital world, everything in digital form is with in the reach of a common man even a poor man also can have access to such digital things. Same way will happen with ‘everything that can be tokenized will be tokenized’. Revolution in Telephones from Landlines to mobiles is great example to predict the future of tokenization.
NFTs : Non-Fungible Tokens
Assets which can substitute one with other without any erosion in value are fungible in nature.
Non fungible assets means two different assets with their different identities or values.

Fungible Assets :
Ex- Two Rs.100 notes are there for you to choose any one, you choose any note of these two because both the notes have same value. There may be five notes of Rs.100 and one note of Rs.500, you are asked to choose either five notes of Rs.100 or one note of Rs.500. You may choose any one because both the situations have same value for you. This is the situation of ‘Fungible assets’.
Non-Fungible Assets :
Ex- Two similar assets are there and you care about to choose which one of these two. Reasons of your such care may be like – different underlying values of these two assets or may be some emotional attachment you have or may be some speculative reason of future or any other reason. Not only two assets but there can be more than two assets for you to make choice. Like you go for shopping for shirts, you choose one or two out of so many shirts due to different reasons like colour, style or quality or brand etc.
Very good example of non-fungible just came to my thought is ‘PARENTS’. Parents are non-fungible. For you or me, Parents can not be the substitute of any other parents.
What is more there in this world – fungible or non-fungible? Quite obvious non-fungible assets are more than fungible in the world. Almost everything is non-fungible in this world.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs):
In case of non-fungible assets, when there is ownership in such assets and such ownership is tokenized, then such tokenization of non-fungible assets is known as NFTs – Non-fungible tokens.
Ex- You bought a car which is non-fungible asset for you due to different reasons. Now, you tokenized the ownership in such car and sold it which means you transferred the ownership of that car to someone else. Or another case if say there is a digital image ownership of which has been tokenized and you bought ownership in that image and paid the amount in tokens, that ownership itself becomes non-fungible token.
NFT is the tokenized representation of non-fungible asset.
The most important aspect of NFTs is their value. How NFTs accrues value?
Simply speaking value comes from demand. Price of a NFT is derived from it’s demand. But, how such demand arises and from where it comes – it’s very important aspect. Specially for investors, it’s important to know about such phenomenon of demand and supply of NFTs.
Value or price of a NFT is derived from the underlying ownership right in the asset. Right to own a NFT is different from right to view NFT. Ex- Popular NFT of an image has a right of ownership in it due to various reasons like who made it/designed it/material used to make it/whose picture or what message in the image. The owner of this image (NFT) may decide to sell at higher price in future which is the speculative reason of deriving demand & value of such NFT or there may be emotional reason for a person to buy/hold/sell such an image (NFT).
Are NFTs a Fad?
Fad means any activity getting popular without any logic. This is the early stage of NFTs, so it’s my assumption that most of the NFTs are Fad and getting popular without any logic. NFTs are very interesting in themselves but with logical use case like in real estate, some games like crypto kitties, for singers, for painters/artists, for sports persons etc.
Future of NFTs : NFTs have great future ahead. Everything that can be tokenized will be tokenized.
NFTs are very important part of catalyst to boost blockchain-powered digital economy. Various projects have been experimented with NFTs in multiple use-cases, including real estates, digital identity, gaming, music, arts, digital homes, digital agriculture business,etc.
How do NFTs work?
There are various frameworks for the creation and issuance of NFTs. ERC-721 is the most famous one standard for creating/issuing/trading NFTs on the Ethereum blockchain. Binance Smart Chain (BSC) is also getting popular for the same service for NFTs and BSC has it’s own NFT standards i.e. BEP-721. At BSC, NFTs costs lesser than what these cost at Ethereum blockchain.
One more latest improved standard is ERC-1155 at ethereum and BEP-1155 at BSC. Beauty of this new standard is that it enables a single contract to contain properties of both fungible and non-fungible tokens which is good for whole NFTs community opening new range of possibilities. It allows high degree of interoperability, which means unique assets can be transferred between different applications with ease.
How to Buy NFTs?
Required elements to buy NFTs are there should be specific cryptocurrency to pay for price of NFTs, crypto wallet (metamask or any other) should be there, account at some NFTs market place. Connect your wallet with the NFT market place so that you can buy NFT from there and pay in desired cryptocurrency (lying in your wallet). After purchase, you will get NFT in your crypto wallet which would work as storage medium also for your NFTs storage management. After the purchase you can transfer your NFT from this crypto wallet to some other crypto wallet that may be more safer place. Before buying, make sure that you are not at the fake market place. To check if market place is genuine or not, you can opt different set mechanisms like website of the market place, coinmarketplace.com, coingecko.com, etc.
You can buy NFTs at any famous market place based at Binance Smart Chain or Ethereum. At BSC, cryptocurrency to pay for NFTs will be in BNB, the native token of BSC. And at ethereum, currency will be ETH to pay for NFTs.
In India, recent launch of NFT market place is from WazirX, the largest crypto exchange. You can buy various NFTs at WazirX NFT market place. You need to have account at WazirX market place and metamask crypto wallet. Connect your wallet with your account at WazirX. Don’t get confused with your WazirX exchange account. It’s different from your exchange account. I am sharing link of WazirX NFT market place for more details on how to operate at WazirX NFT market place.
Use cases for NFTs
NFTs can be used in various fields like collectible items, investment products, social tokens or fan tokens (recently Indian film actor Salman khan launched his own NFTs), real estate, gaming, agricultural mandis, music industry, art industry, etc.
To be little more elaborative on use cases, the story of CryptoKitties is must to go through to understand more about the NFTs how it became more famous about to tokenize the various non-fungible assets in the physical world.
The story of CryptoKitties and Ethereum
CryptoKitties is an early example of blockchain and NFT use case during 2017. CryptoKitties is a game built on Ethereum blockchain that allows players to collect , breed, and exchange virtual cats. I don’t think before 2017 we had imagined to breed cats virtually. Every CryptoKitty has a combination of several different properties like age, breed, or color etc. Each of them is unique and can’t be interchanged with each other. Every CryptoKitty is indivisible, which means there is no way to divide a CryptoKitty token in to smaller parts. In 2017, it became the reason for high congestion at Ethereum network and 25% of ethereum’s network was from such cats.
Let’s discuss some popular FAQs about NFTs :
What is Minting in NFTs ?
Minting is a process of tokenizing an asset and creating NFT. This can be done by the owner/creator of work or by a person/firm authorised by the owner/creator.
Example – You can read a book but you can not translate it in to another language for commercial purpose. But you can do it if you get intellectual property rights(IPRs) from the author of the book to translate it for commercial purpose. If you tokenize such IPRs and create NFT of the said book’s translated version for commercial purpose, then it falls under the category of NFT minting. Here, author of the book also can mint NFT of the book and sell it for commercial purpose.
What are the legal rights of the buyer of NFT?
Depending upon NFT, the buyer may get rights to own, sell or lend or monetize etc.
Why do we need NFTs in IP market ?
Intellectual property market has complex licensing system with huge paper work. NFTs route enable quick tokenization & monetization of IP.
What are the types of NFTs
NFTs can be of many types, including:
- Art,
- Collectibles (trading cards, sneakers)
- Domains,
- Financial instruments
- IP assets – trademarks, patents etc
- Music,
- Photos,
- Tokenized assets (cars, land, oil, real estates)
- Videos of iconic events
- Virtual game items (avatars, skins, weapons, etc)
Some Popular characteristics of NFTs are :
Standardization ; Interoperability ; Tradeability ; Liquidity ; Immutability & provable scarcity ; Programmability
NFT Standards
ERC-721
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/tokens/erc-721/
ERC-1155
https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-1155
ERC-998
https://github.com/ethereum/eips/issues/998
dGoods


 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  USDC
USDC  Solana
Solana  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Litecoin
Litecoin  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Polkadot
Polkadot  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic  PancakeSwap
PancakeSwap  Decentraland
Decentraland  GALA
GALA  IoTeX
IoTeX  BUSD
BUSD